How to Fix a Slow Computer? My 5-Minute Troubleshooting Routine
A slow computer doesn’t always mean it’s time for a new one.
Before you reinstall Windows or buy new hardware, try this quick 5-minute routine I use when diagnosing slow PCs for my coworkers.
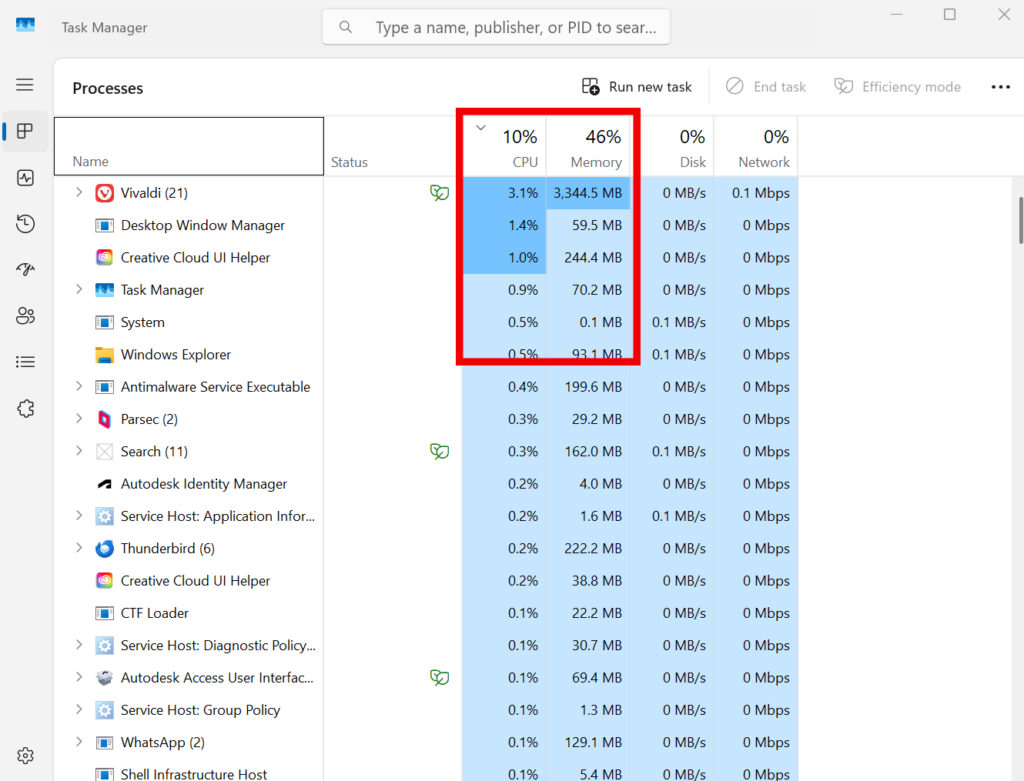
1. Check Resource Usage
Open Task Manager with
Ctrl + Shift + Esc
or
Ctrl + Alt + Del and then select Task Manager
Sort the tasks by CPU usage or RAM usage and look for apps that are taking up a lot of resources. Don’t just close everything – note what is consistently heavy.
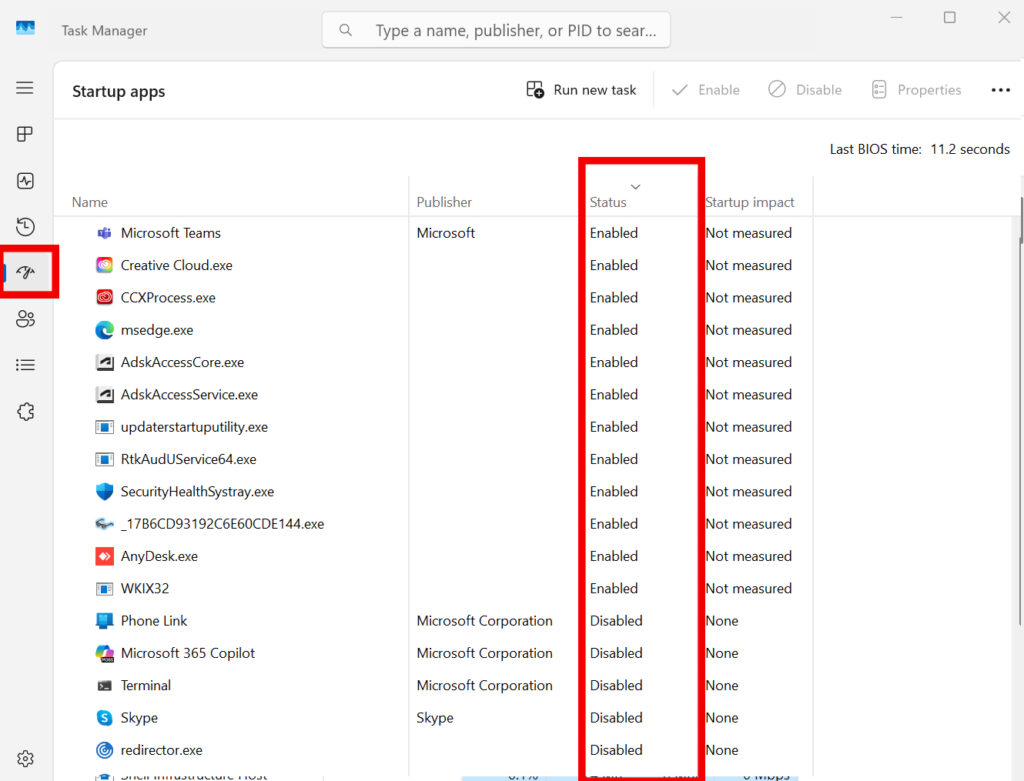
2. Clean Up Startup Apps
Don’t close Task Manager yet.
Go to the Startup Apps tab in Task Manager.
Disable anything that doesn’t need to run on every boot.
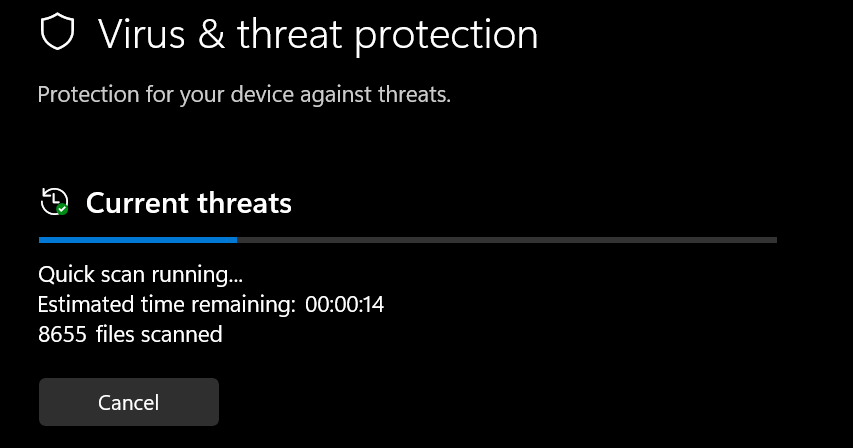
3. Scan for Malware & Viruses
Malware can silently consume CPU, memory, and disk resources.
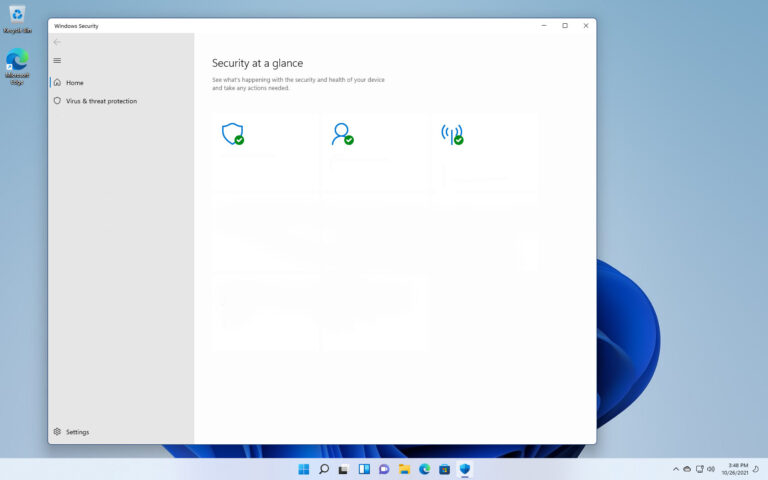
Use your antivirus or Windows Security to scan:
1. Open Windows Security → Virus & Threat Protection (Windows Security is very good as of 2025)
2. Click Quick Scan (or Full Scan if time allows)
3. Quarantine or remove any threats
4. Use Malwarebytes or other trusted tools for a second opinion. Install it and run it once. Clean what it finds and then you can uninstall it! I recommend this tool!
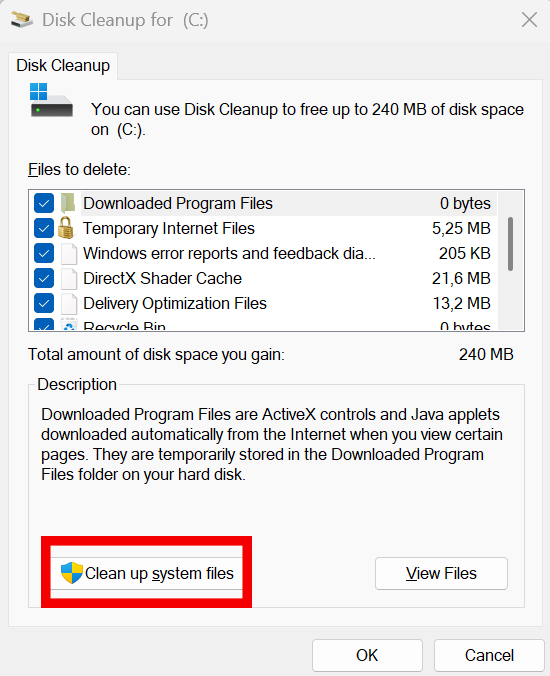
4. Clear Temporary Files
Open Run (Win + R), type:
cleanmgr
Select your system drive (usually C:) and check:
– Temporary Files
– Windows Update Cleanup
– Recycle Bin
And then click OK
You can also click Clean up System Files and the Cleanup Utility will restart and you choose to delete some temporary system files that you don’t need and old versions of your Windows!
5. Repair System Files
If performance dropped suddenly, corrupted files could be the cause.
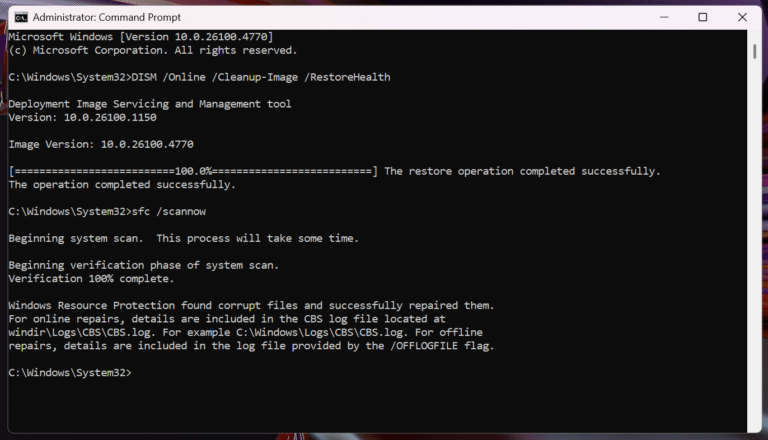
Open Command Prompt (Admin) and run:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
sfc /scannow
Let both commands finish completely. This step often resolves hidden issues after failed updates or malware cleanup. You can read more about it here.
6. Check Hardware Health
If software cleanup doesn’t help, hardware may be the bottleneck.
Check for:
- HDD vs SSD: Upgrade to SSD for instant performance boost.
- RAM: Minimum 8 GB; 16 GB recommended for multitasking.
- Thermals: Dust buildup or weak cooling can cause throttling.
Use tools like HWInfo, CoreTemp, or CrystalDiskInfo to verify component health.
Conclusion
A slow computer often has layers of small issues — not one big cause.
The key skill is learning to diagnose efficiently: